测试代码:
package com.github.abel533.event;import com.github.abel533.C;import org.springframework.context.ApplicationEvent;import org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener;import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;/** * @author liuzh */@Componentpublic class ApplicationListenerImpl implements ApplicationListener<ApplicationEvent> { public ApplicationListenerImpl() { C.print("ApplicationListenerImpl#constructor"); } @Override public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationEvent event) { C.print("ApplicationListener#" + event.getClass().getSimpleName()); }}
package com.github.abel533.event;import com.github.abel533.lifecycle.BeanLifecycle;import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;@SpringBootApplicationpublic class ListenerApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(ListenerApplication.class, args).close(); }}
用以上代码实现 ApplicationListener 接口,输出所有事件。
当以 @Component 方式配置时
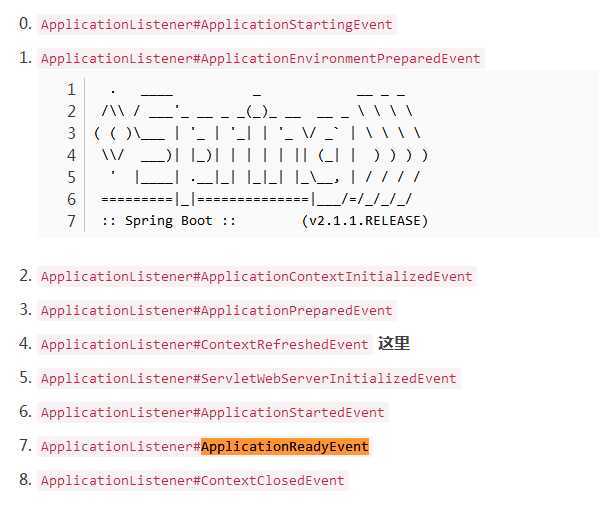
事件触发顺序如下:
ApplicationListener#ContextRefreshedEvent
ApplicationListener#ServletWebServerInitializedEvent
ApplicationListener#ApplicationStartedEvent
ApplicationListener#ApplicationReadyEvent
ApplicationListener#ContextClosedEvent
当通过 /META-INF/spring.factories 配置时
配置内容如下:
org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener=com.github.abel533.event.ApplicationListenerImpl
此时输出的事件顺序如下:
差异
很容易通过对比发现,Event 触发的时间极早,以至于 @Component 方式只能从第 4 个事件才开始获取到。
从这两种方式的加载时机来看这个差异产生的原因。
在 SpringApplication 构造方法中,就调用 getSpringFactoriesInstances 来获取 /META-INF/spring.factories 配置的 ApplicationListener,代码如下:
public SpringApplication(ResourceLoader resourceLoader, Class<?>... primarySources) { this.resourceLoader = resourceLoader; Assert.notNull(primarySources, "PrimarySources must not be null"); this.primarySources = new LinkedHashSet<>(Arrays.asList(primarySources)); this.webApplicationType = WebApplicationType.deduceFromClasspath(); setInitializers((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances( ApplicationContextInitializer.class)); setListeners((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationListener.class)); this.mainApplicationClass = deduceMainApplicationClass();}
在 SpringFactoriesLoader#loadFactoryNames 实现了从该配置文件获取实现名的方法。从这之后就能收到后续触发的事件。
通过 @Component 方式时,在 SpringApplication#refresh 中调用 registerListeners 获取的所有 ApplicationListener 接口的实现。代码如下:
@Override public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException { synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) { try { // 注册所有 ApplicationListener 实现 registerListeners(); // Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons. finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory); // 这里会触发 ContextRefreshedEvent finishRefresh(); } } }
下面先分析前 4 个无法获取的事件顺序。
ApplicationStartingEvent
第 0 个事件是在 EventPublishingRunListener#starting 中发布的,代码如下:
@Overridepublic void starting() { this.initialMulticaster.multicastEvent( new ApplicationStartingEvent(this.application, this.args));}
此时的堆栈调用情况如下:
onApplicationEvent:15, ApplicationListenerImpl (com.github.abel533.event)doInvokeListener:172, SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster (org.springframework.context.event)invokeListener:165, SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster (org.springframework.context.event)multicastEvent:139, SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster (org.springframework.context.event)multicastEvent:127, SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster (org.springframework.context.event)starting:69, EventPublishingRunListener (org.springframework.boot.context.event)starting:48, SpringApplicationRunListeners (org.springframework.boot)run:302, SpringApplication (org.springframework.boot)run:1260, SpringApplication (org.springframework.boot)run:1248, SpringApplication (org.springframework.boot)main:12, ListenerApplication (com.github.abel533.event)
ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent
第 1 个事件是在 EventPublishingRunListener#environmentPrepared 中发布的,代码如下:
@Overridepublic void environmentPrepared(ConfigurableEnvironment environment) { this.initialMulticaster.multicastEvent(new ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent( this.application, this.args, environment));}
此时的堆栈调用情况如下:
onApplicationEvent:15, ApplicationListenerImpl (com.github.abel533.event)doInvokeListener:172, SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster (org.springframework.context.event)invokeListener:165, SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster (org.springframework.context.event)multicastEvent:139, SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster (org.springframework.context.event)multicastEvent:127, SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster (org.springframework.context.event)environmentPrepared:75, EventPublishingRunListener (org.springframework.boot.context.event)environmentPrepared:54, SpringApplicationRunListeners (org.springframework.boot)prepareEnvironment:347, SpringApplication (org.springframework.boot)run:306, SpringApplication (org.springframework.boot)run:1260, SpringApplication (org.springframework.boot)run:1248, SpringApplication (org.springframework.boot)main:12, ListenerApplication (com.github.abel533.event)
ApplicationContextInitializedEvent
第 2 个事件是在 EventPublishingRunListener#contextPrepared 中发布的,代码如下:
@Overridepublic void contextPrepared(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) { this.initialMulticaster.multicastEvent(new ApplicationContextInitializedEvent( this.application, this.args, context));}
此时的堆栈调用情况如下:
onApplicationEvent:15, ApplicationListenerImpl (com.github.abel533.event)doInvokeListener:172, SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster (org.springframework.context.event)invokeListener:165, SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster (org.springframework.context.event)multicastEvent:139, SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster (org.springframework.context.event)multicastEvent:127, SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster (org.springframework.context.event)contextPrepared:81, EventPublishingRunListener (org.springframework.boot.context.event)contextPrepared:60, SpringApplicationRunListeners (org.springframework.boot)prepareContext:374, SpringApplication (org.springframework.boot)run:314, SpringApplication (org.springframework.boot)run:1260, SpringApplication (org.springframework.boot)run:1248, SpringApplication (org.springframework.boot)main:12, ListenerApplication (com.github.abel533.event)
ApplicationPreparedEvent
第 3 个事件是在 EventPublishingRunListener#contextLoaded 中发布的,代码如下:
@Overridepublic void contextLoaded(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) { for (ApplicationListener<?> listener : this.application.getListeners()) { if (listener instanceof ApplicationContextAware) { ((ApplicationContextAware) listener).setApplicationContext(context); } context.addApplicationListener(listener); } this.initialMulticaster.multicastEvent( new ApplicationPreparedEvent(this.application, this.args, context));}
此时的堆栈调用情况如下:
onApplicationEvent:15, ApplicationListenerImpl (com.github.abel533.event)doInvokeListener:172, SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster (org.springframework.context.event)invokeListener:165, SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster (org.springframework.context.event)multicastEvent:139, SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster (org.springframework.context.event)multicastEvent:127, SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster (org.springframework.context.event)contextLoaded:93, EventPublishingRunListener (org.springframework.boot.context.event)contextLoaded:66, SpringApplicationRunListeners (org.springframework.boot)prepareContext:393, SpringApplication (org.springframework.boot)run:314, SpringApplication (org.springframework.boot)run:1260, SpringApplication (org.springframework.boot)run:1248, SpringApplication (org.springframework.boot)main:12, ListenerApplication (com.github.abel533.event)
ContextRefreshedEvent
在上面差异中提到 finishRefresh 会触发 ContextRefreshedEvent,代码如下:
@Overrideprotected void finishRefresh() { super.finishRefresh(); WebServer webServer = startWebServer(); if (webServer != null) { publishEvent(new ServletWebServerInitializedEvent(webServer, this)); }}
注意 super.finishRefresh,代码如下(有删减):
protected void finishRefresh() { // Publish the final event. publishEvent(new ContextRefreshedEvent(this));}
ServletWebServerInitializedEvent
注意前面 finishRefresh 方法,如果存在 webServer != null,就会发布 ServletWebServerInitializedEvent。
ApplicationStartedEvent
在 SpringApplication#run 方法中,执行完成后,就会调用 listeners.started(context); 方法,在这里面会发布 ApplicationStartedEvent。
ApplicationReadyEvent
和上面 ApplicationStartedEvent 一样,如下代码(有删减):
// ApplicationStartedEventlisteners.started(context);callRunners(context, applicationArguments);// ApplicationReadyEventlisteners.running(context);
执行完所有 ApplicationRunner 和 CommandLineRunner 接口方法后,就会调用 listeners.running(context),在这里面就会发布 ApplicationReadyEvent。
在这之后就没有运行期的主要事件了(不考虑 devtools 重启)。在这个事件里,可以请求zookeeper进行服务注册,以便其它服务发现并调用它等相关操作。
ContextClosedEvent
当调用关闭方法的时候,自然就触发了 ContextClosedEvent,调用堆栈如下:
onApplicationEvent:20, ApplicationListenerImpl (com.github.abel533.event)doInvokeListener:172, SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster (org.springframework.context.event)invokeListener:165, SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster (org.springframework.context.event)multicastEvent:139, SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster (org.springframework.context.event)publishEvent:398, AbstractApplicationContext (org.springframework.context.support)publishEvent:355, AbstractApplicationContext (org.springframework.context.support)doClose:994, AbstractApplicationContext (org.springframework.context.support)close:961, AbstractApplicationContext (org.springframework.context.support)main:12, ListenerApplication (com.github.abel533.event)
本文转自:https://blog.csdn.net/isea533/article/details/100146833