这周的 Cassidoo 的每周简讯有这么一个面试题::
写一个函数,这个函数接收一个正确的 JSON 字符串并将其转化为一个对象(或字典,映射等,这取决于你选择的语言)。示例输入:
fakeParseJSON('{ "data": { "fish": "cake", "array": [1,2,3], "children": [ { "something": "else" }, { "candy": "cane" }, { "sponge": "bob" } ] } } ')
当时,我想这么写:
const fakeParseJSON = JSON.parse;但是,我想起之前写了一些关于AST的文章,
其中涵盖了编译器管道的概述以及如何操作AST,但是我没有过多介绍如何实现解析器。因为实现JavaScript编译器对我来说是一项艰巨的任务。
那就没必要担心。 JSON也是一种语言,有自己的语法,可以参考规范。 根据编写JSON解析器所需的知识和技术转移到编写JS解析器中。
好了,那就开始编写一个JSON解析器吧。
查看规范文档页面,可以看到以下两个图。
json elementvalue object array string number "true" "false" "null"object '{' ws '}' '{' members '}'两个图其实是等价的。
一个基于视觉,一个基于文本。基于文本语法的语法 —— 巴科斯-诺尔范式,通常被提供给另一个解析这种语法并为其生成解析器的解析器,终于说到解析器了!??
在这篇文章中,我们重点关注铁路图上,因为它是可视化的,看起来更友好。
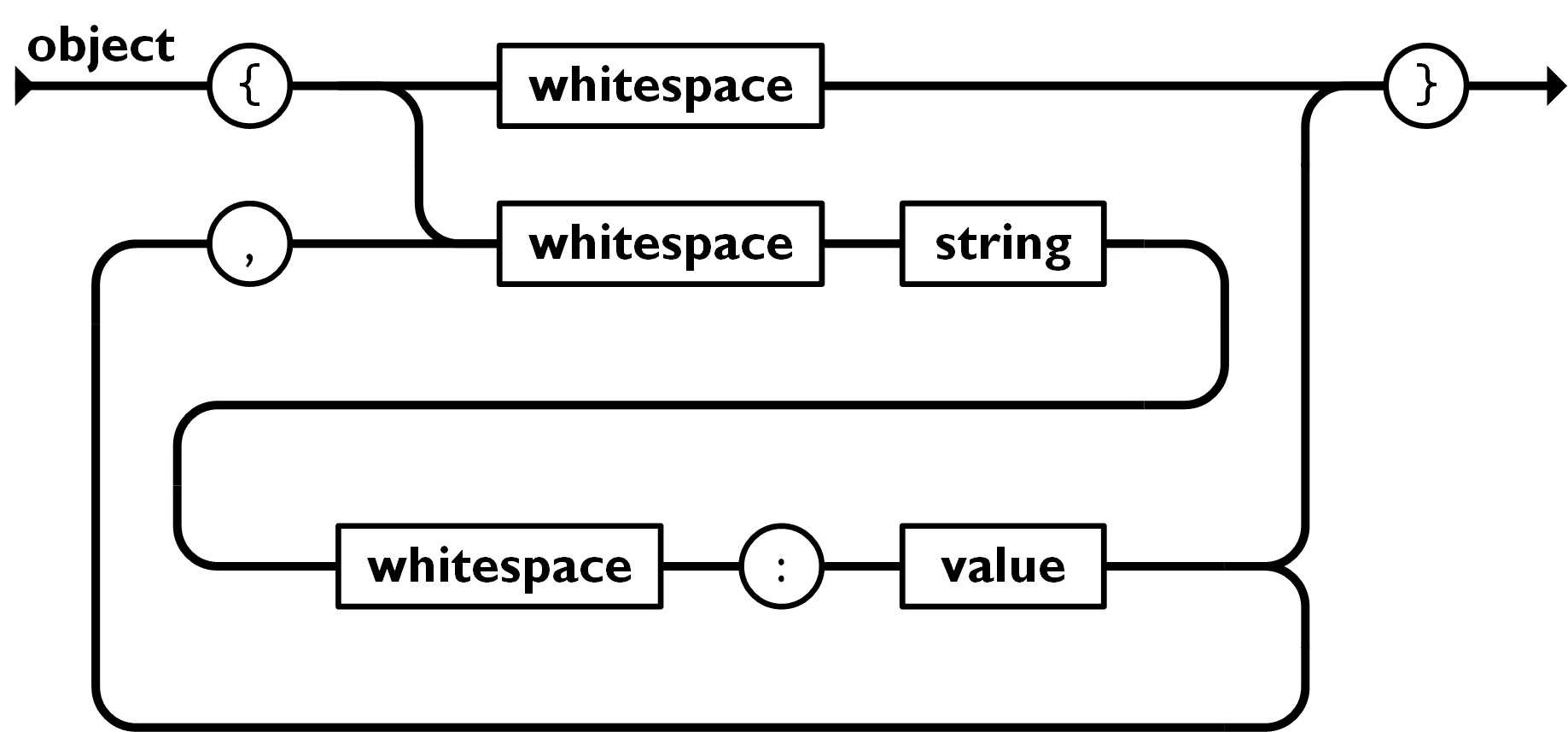
先来看下第一张的铁路图:

所以这就是JSON中“object”的语法。
从左侧开始,沿着箭头的方向走,一直到右侧为止。
圆圈里面是一个字符,例如 {,,,:,},矩形里面是其它语法的占位符,例如 whitespace(空格)、string 和 value。因此要解析"whitespace",我们需要查阅"whitepsace"语法。
因此,对于一个对象而言,从左边开始,第一个字符必须是一个左花括号 {,然后往下走会有两种情况:
whitespace → } → 结束whitespace → string → whitespace → : → value → } → 结束当然当抵达value的时候,你可以选择继续下去:
} → 结束,或者, → whitespace → … → value} → 结束。下面我们开始编写代码,代码结构如下:
function fakeParseJSON(str) { let i = 0; // TODO}初始化 i 将其作为当前字符的索引值,只要 i 值到达 str 的长度,我们就会结束函数。
后面我们来实现“object”语法:
function fakeParseJSON(str) { let i = 0; function parseObject() { if (str[i] === '{') { i++; skipWhitespace(); // 如果不是 '}', // 我们接收 string -> whitespace -> ':' -> value -> ... 这样的路径字符串 while (str[i] !== '}') { const key = parseString(); skipWhitespace(); eatColon(); const value = parseValue(); } } }}我们可以调用 parseObject 来解析类似string和whitespace之类的语法,只要我们实现这些功能,一切都解决了??。
还有就是我我忘记加逗号,了。逗号,只会出现在开始第二次whitespace → string → whitespace → : → … 循环之前。
在这个基础上,我们加上了一下几行:
function fakeParseJSON(str) { let i = 0; function parseObject() { if (str[i] === '{') { i++; skipWhitespace(); let initial = true; // 如果不是 '}', // 就按照这样的路径执行: string -> whitespace -> ':' -> value -> ... while (str[i] !== '}') { if (!initial) { eatComma(); skipWhitespace(); } const key = parseString(); skipWhitespace(); eatColon(); const value = parseValue(); initial = false; } // move to the next character of '}' i++; } }}一些命名上的约定:
parseSomethingeatSomethingskipSomething下面来实现eatComma和eatColon
function fakeParseJSON(str) { // ... function eatComma() { if (str[i] !== ',') { throw new Error('Expected ",".'); } i++; } function eatColon() { if (str[i] !== ':') { throw new Error('Expected ":".'); } i++; }}到目前为止,我们实现了parseObject的语法,但是这个解析函数的返回值是什么呢?
不错,我们需要返回一个JavaScript对象:
function fakeParseJSON(str) { let i = 0; function parseObject() { if (str[i] === '{') { i++; skipWhitespace(); const result = {}; let initial = true; // 如果不是 '}', // 就按照这样的路径执行: string -> whitespace -> ':' -> value -> ... while (str[i] !== '}') { if (!initial) { eatComma(); skipWhitespace(); } const key = parseString(); skipWhitespace(); eatColon(); const value = parseValue(); result[key] = value; initial = false; } // 移动到下一个字符 '}' i++; return result; } }}现在你已经看到我怎么去实现“object“语法,现在是时候让你尝试一下”array“语法了:
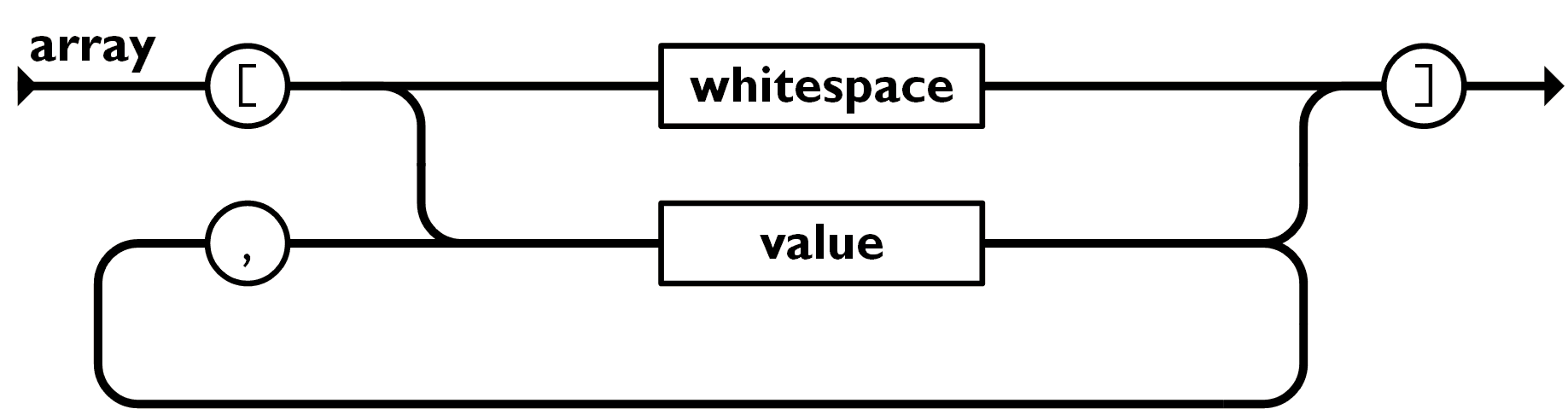
function fakeParseJSON(str) { // ... function parseArray() { if (str[i] === '[') { i++; skipWhitespace(); const result = []; let initial = true; while (str[i] !== ']') { if (!initial) { eatComma(); } const value = parseValue(); result.push(value); initial = false; } // 移动到下一个字符 ']' i++; return result; } }}现在,我们来看一个更有趣的语法,“value”:
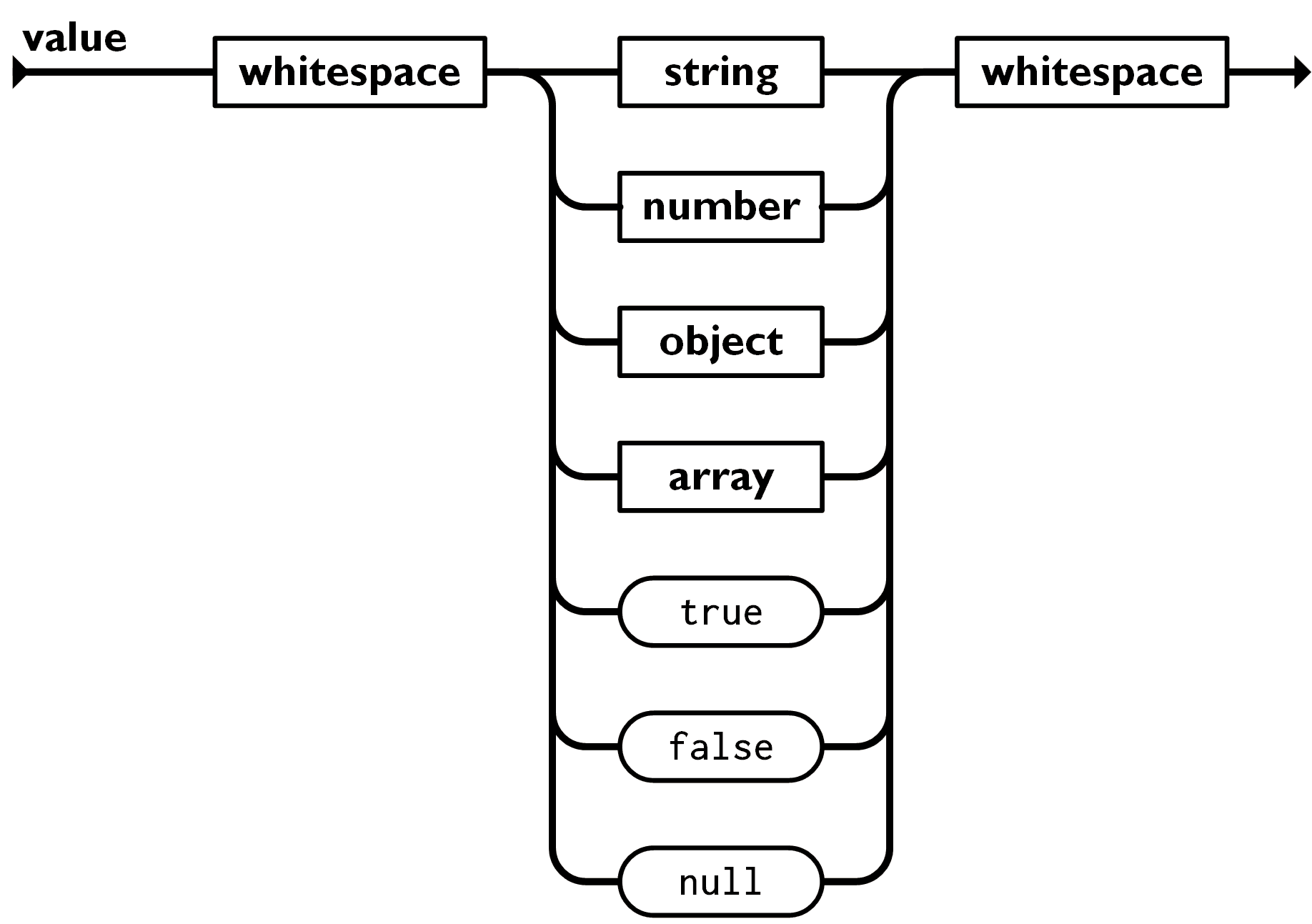
如上图的路径:
一个值是以“whitespace”开始,然后接着是以下类型的一种:“string”,“number”,“object”,“array”,“true”,“false” 或者null,最后以一个“whitespace”结束。
function fakeParseJSON(str) { // ... function parseValue() { skipWhitespace(); const value = parseString() ?? parseNumber() ?? parseObject() ?? parseArray() ?? parseKeyword('true', true) ?? parseKeyword('false', false) ?? parseKeyword('null', null); skipWhitespace(); return value; }}这个??叫做空值合并运算符,它类似我们用来设置默认值 foo || default 中的 ||,只要foo是假值,|| 就会返回 default, 而空值合并运算符只会在 foo 为 null 或 undefined 时返回 default。可以看个例子:
const foo = null ?? 'default string';console.log(foo);// 输出: "default string"parseKeyword 将检查当前 str.slice(i) 是否与关键字字符串匹配,如果匹配,将返回关键字值:
function fakeParseJSON(str) { // ... function parseKeyword(name, value) { if (str.slice(i, i + name.length) === name) { i += name.length; return value; } }}这个就是parseKeyword的实现。
我们还有 3 个以上的语法要实现,但我为了控制文章篇幅,在下面的 CodeSandbox 中实现这些语法。
CodeSandbox
完成所有语法实现之后,然后返回由parseValue返回的json值:
function fakeParseJSON(str) { let i = 0; return parseValue(); // ...}就是这样!
好了,还没有那么快完成朋友,我们只是完成的理想的部分,那么非理想的部分呢?
作为一个优秀的开发人员,我们也需要优雅地处理非理想情况。对于解析器,这意味着使用适当的错误消息大声警告开发人员。
让我们来处理两个最常见的错误情况:
在所有的 while 循环中,例如 parseObject 中的 while 循环:
function fakeParseJSON(str) { // ... function parseObject() { // ... while(str[i] !== '}') {我们需要确保访问的字符不会超过字符串的长度。这发生在字符串意外结束时,而我们仍然在等待一个结束字符 —— }。比如说下面的例子:
function fakeParseJSON(str) { // ... function parseObject() { // ... while (i < str.length && str[i] !== '}') { // ... } checkUnexpectedEndOfInput(); // move to the next character of '}' i++; return result; }}你还记得当你还是一个初级开发者的时候,每次遇到一些不清晰的语法错误的时候,你完全不知道哪里出问题了?
现在你有经验了,是时候停止这种恶性循环和吐槽了。
Unexpected token "a"例如以上的错误,只会让用户很困惑地盯着屏幕,而不知道错误在哪里。
相比去吐槽,其实有很多更好的方式去改善这些错误提示,下面有几点建议可以考虑加到解析器里面:
标准关键字对用户谷歌寻求帮助很有用
// 不好的提示Unexpected token "a"Unexpected end of input// 好的提示JSON_ERROR_001 Unexpected token "a"JSON_ERROR_002 Unexpected end of input像 Babel 这样的解析器,会向你显示一个代码框架,它是一个带有下划线、箭头或突出显示错误的代码片段
// 不好的提示Unexpected token "a" at position 5// 好的提示{ "b"a ^JSON_ERROR_001 Unexpected token "a"一个如何输出代码片段的例子:
function fakeParseJSON(str) { // ... function printCodeSnippet() { const from = Math.max(0, i - 10); const trimmed = from > 0; const padding = (trimmed ? 3 : 0) + (i - from); const snippet = [ (trimmed ? '...' : '') + str.slice(from, i + 1), ' '.repeat(padding) + '^', ' '.repeat(padding) + message, ].join('\n'); console.log(snippet); }}可以的话,可以说明是哪里出问题以及给出修复建议。
// 不好的提示Unexpected token "a" at position 5// 好的提示{ "b"a ^JSON_ERROR_001 Unexpected token "a".Expecting a ":" over here, eg:{ "b": "bar" } ^You can learn more about valid JSON string in http://goo.gl/xxxxx如果可能,根据解析器目前收集的上下文提供建议
fakeParseJSON('"Lorem ipsum');// instead ofExpecting a `"` over here, eg:"Foo Bar" ^// showExpecting a `"` over here, eg:"Lorem ipsum" ^基于上下文的建议会让人感觉更有关联性和可操作性。 记住所有的建议,用以下几点检查已经更新的CodeSandbox
推荐阅读Evan Czaplicki的关于如何提高编译器用户体验的一篇文章“编译器错误建议”
function fakeParseJSON(str) { let i = 0; const value = parseValue(); expectEndOfInput(); return value; function parseObject() { if (str[i] === "{") { i++; skipWhitespace(); const result = {}; let initial = true; // if it is not '}', // we take the path of string -> whitespace -> ':' -> value -> ... while (i < str.length && str[i] !== "}") { if (!initial) { eatComma(); skipWhitespace(); } const key = parseString(); if (key === undefined) { expectObjectKey(); } skipWhitespace(); eatColon(); const value = parseValue(); result[key] = value; initial = false; } expectNotEndOfInput("}"); // move to the next character of '}' i++; return result; } } function parseArray() { if (str[i] === "[") { i++; skipWhitespace(); const result = []; let initial = true; while (i < str.length && str[i] !== "]") { if (!initial) { eatComma(); } const value = parseValue(); result.push(value); initial = false; } expectNotEndOfInput("]"); // move to the next character of ']' i++; return result; } } function parseValue() { skipWhitespace(); const value = parseString() ?? parseNumber() ?? parseObject() ?? parseArray() ?? parseKeyword("true", true) ?? parseKeyword("false", false) ?? parseKeyword("null", null); skipWhitespace(); return value; } function parseKeyword(name, value) { if (str.slice(i, i + name.length) === name) { i += name.length; return value; } } function skipWhitespace() { while ( str[i] === " " || str[i] === "\n" || str[i] === "\t" || str[i] === "\r" ) { i++; } } function parseString() { if (str[i] === '"') { i++; let result = ""; while (i < str.length && str[i] !== '"') { if (str[i] === "\\") { const char = str[i + 1]; if ( char === '"' || char === "\\" || char === "/" || char === "b" || char === "f" || char === "n" || char === "r" || char === "t" ) { result += char; i++; } else if (char === "u") { if ( isHexadecimal(str[i + 2]) && isHexadecimal(str[i + 3]) && isHexadecimal(str[i + 4]) && isHexadecimal(str[i + 5]) ) { result += String.fromCharCode( parseInt(str.slice(i + 2, i + 6), 16) ); i += 5; } else { i += 2; expectEscapeUnicode(result); } } else { expectEscapeCharacter(result); } } else { result += str[i]; } i++; } expectNotEndOfInput('"'); i++; return result; } } function isHexadecimal(char) { return ( (char >= "0" && char <= "9") || (char.toLowerCase() >= "a" && char.toLowerCase() <= "f") ); } function parseNumber() { let start = i; if (str[i] === "-") { i++; expectDigit(str.slice(start, i)); } if (str[i] === "0") { i++; } else if (str[i] >= "1" && str[i] <= "9") { i++; while (str[i] >= "0" && str[i] <= "9") { i++; } } if (str[i] === ".") { i++; expectDigit(str.slice(start, i)); while (str[i] >= "0" && str[i] <= "9") { i++; } } if (str[i] === "e" || str[i] === "E") { i++; if (str[i] === "-" || str[i] === "+") { i++; } expectDigit(str.slice(start, i)); while (str[i] >= "0" && str[i] <= "9") { i++; } } if (i > start) { return Number(str.slice(start, i)); } } function eatComma() { expectCharacter(","); i++; } function eatColon() { expectCharacter(":"); i++; } // error handling function expectNotEndOfInput(expected) { if (i === str.length) { printCodeSnippet(`Expecting a \`${expected}\` here`); throw new Error("JSON_ERROR_0001 Unexpected End of Input"); } } function expectEndOfInput() { if (i < str.length) { printCodeSnippet("Expecting to end here"); throw new Error("JSON_ERROR_0002 Expected End of Input"); } } function expectObjectKey() { printCodeSnippet(`Expecting object key hereFor example:{ "foo": "bar" } ^^^^^`); throw new Error("JSON_ERROR_0003 Expecting JSON Key"); } function expectCharacter(expected) { if (str[i] !== expected) { printCodeSnippet(`Expecting a \`${expected}\` here`); throw new Error("JSON_ERROR_0004 Unexpected token"); } } function expectDigit(numSoFar) { if (!(str[i] >= "0" && str[i] <= "9")) { printCodeSnippet(`JSON_ERROR_0005 Expecting a digit hereFor example:${numSoFar}5${" ".repeat(numSoFar.length)}^`); throw new Error("JSON_ERROR_0006 Expecting a digit"); } } function expectEscapeCharacter(strSoFar) { printCodeSnippet(`JSON_ERROR_0007 Expecting escape characterFor example:"${strSoFar}\\n"${" ".repeat(strSoFar.length + 1)}^^List of escape characters are: \\", \\\\, \\/, \\b, \\f, \\n, \\r, \\t, \\u`); throw new Error("JSON_ERROR_0008 Expecting an escape character"); } function expectEscapeUnicode(strSoFar) { printCodeSnippet(`Expect escape unicodeFor example:"${strSoFar}\\u0123${" ".repeat(strSoFar.length + 1)}^^^^^^`); throw new Error("JSON_ERROR_0009 Expecting an escape unicode"); } function printCodeSnippet(message) { const from = Math.max(0, i - 10); const trimmed = from > 0; const padding = (trimmed ? 4 : 0) + (i - from); const snippet = [ (trimmed ? "... " : "") + str.slice(from, i + 1), " ".repeat(padding) + "^", " ".repeat(padding) + message ].join("\n"); console.log(snippet); }}// console.log("Try uncommenting the fail cases and see their error message");// console.log("↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓");// Fail cases:printFailCase("-");printFailCase("-1.");printFailCase("1e");printFailCase("-1e-2.2");printFailCase("{");printFailCase("{}{");printFailCase('{"a"');printFailCase('{"a": "b",');printFailCase('{"a":"b""c"');printFailCase('{"a":"foo\\}');printFailCase('{"a":"foo\\u"}');printFailCase("[");printFailCase("[][");printFailCase("[[]");printFailCase('["]');function printFailCase(json) { try { console.log(`fakeParseJSON('${json}')`); fakeParseJSON(json); } catch (error) { console.error(error); }}要实现解析器,你需要从语法开始。
你可以用铁路图或巴科斯-诺尔范式来使语法正式化。设计语法是最困难的一步。
一旦你解决了语法问题,就可以开始基于语法实现解析器。
错误处理很重要,更重要的是要有有意义的错误消息,以便用户知道如何修复它。
现在,你已经了解了如何实现简单的解析器,现在应该关注更复杂的解析器了:
最后,请关注 @cassidoo,她的每周简讯棒极了。
(完)
以上译文仅用于学习交流,水平有限,难免有错误之处,敬请指正。如果觉得文章对你有帮助,请点个赞吧。