在单核单线程系统中有两个问题:1. 如果系统需要执行某些长时间任务或死循环,就没办法响应其他任何,造成系统“假死”;2.当系统重启或任务崩溃的时候所有的数据都丢失。
针对第一个问题:多线程解决,线程的职责是对CPU进行虚拟化。所有线程共享物理CPU,Windows在某个一个时刻只将一个线程分配给CPU,一个时刻称为时间片quantum,时间一到,Windows就进行上下文切换到另一个线程。
针对第二个问题:进程解决,每个进程都被赋予一个虚拟地址控件,一个进程中使用的代码和数据不能被另一个进程使用。
Windows只能调度线程, 不能调度进程。
线程有以下几个要素:
所有线程共享物理CPU,Windows在某个一个时刻只将一个线程分配给CPU,一个时刻称为时间片quantum(大概30ms,取决于CPU架构),时间一到,Windows就进行上下文切换到另一个线程。
上下文切换时Windows的操作:
上下文切换还有一个操作是:CPU高速缓存的中的数据存到RAM中,新线程执行前从RAM中将数据存储到CPU高速缓存中。
线程可以提前终止时间片,什么也不做。如等待用户输入。只有用户输入的时候,CPU才会调用该线程。
垃圾回收的时候CLR会挂起所有线程。
结论:尽量少使用线程,线程上下文切换和其他的一些操作消耗了大量时间和内存。但有的时候又必须使用线程。
可以查看windows的进程和线程情况:任务选项卡-性能;详细信息。
CPU的发展正在面临着:多个CPU,超线程芯片,多核芯片。
CLR线程就是映射的Windows线程的逻辑线程,完全等价。在以前Microsoft做过一些努力使得CLR线程做一些额外的操作,但是失败了。
必须要避免创建线程来执行异步的操作,相反需要使用线程池执行异步的操作。
有一些特殊情况需要创建线程:
using System;using System.Threading;public static class ThreadBasics { public static void Main() { FirstThread.Go(); BackgroundDemo.Go(true); BackgroundDemo.Go(false); }}internal static class FirstThread { public static void Go() { Console.WriteLine("Main thread: starting a dedicated thread " + "to do an asynchronous operation"); Thread dedicatedThread = new Thread(ComputeBoundOp); dedicatedThread.Start(5); Console.WriteLine("Main thread: Doing other work here..."); Thread.Sleep(10000); // Simulating other work (10 seconds) dedicatedThread.Join(); // Wait for thread to terminate Console.ReadLine(); } // This method's signature must match the ParametizedThreadStart delegate private static void ComputeBoundOp(Object state) { // This method is executed by another thread Console.WriteLine("In ComputeBoundOp: state={0}", state); Thread.Sleep(1000); // Simulates other work (1 second) // When this method returns, the dedicated thread dies }}internal static class BackgroundDemo { public static void Go(Boolean background) { // Create a new thread (defaults to Foreground) Thread t = new Thread(new ThreadStart(ThreadMethod)); // Make the thread a background thread if desired if (background) t.IsBackground = true; t.Start(); // Start the thread return; // NOTE: the application won't actually die for about 10 seconds } private static void ThreadMethod() { Thread.Sleep(10000); // Simulate 10 seconds of work Console.WriteLine("ThreadMethod is exiting"); }}可以使用Microsoft Spy++工具查看线程的调度情况。在vs开发人员命名提示里输入spyxx就可以启动
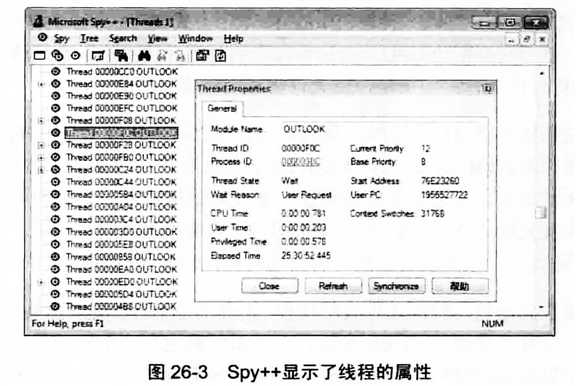
Windows系统又称为抢占式多线程操作系统(preemptive multithreaded)。同时Windows不是实时操作系统。
每个线程都分配了从0(最低)到31(最高)的优先级。Windows先以轮流(round-robin)方法调用所有高优先级线程,直到该优先级所有线程不需要运行,才会调度下一层优先级中的线程。如果在执行低优先级线程的时候,有高优先级的线程需要运行,系统会立刻挂起(暂停)低优先级然后调度高优先级。
系统有一个零页线程(zero page thread),在系统没有线程需要运行的时候,零页线程负责将系统的RAM所有空闲页清零。
为了更好的规划优先级,Microsoft将进程和线程都划分了优先级类:进程:Idle,Below Normal,Normal,Above Normal,High,Realtime;线程:Idle,Lowest,Below Normal,Normal,Above Normal,Highest,Time-Critical。
优先级类与优先级的对应关系:
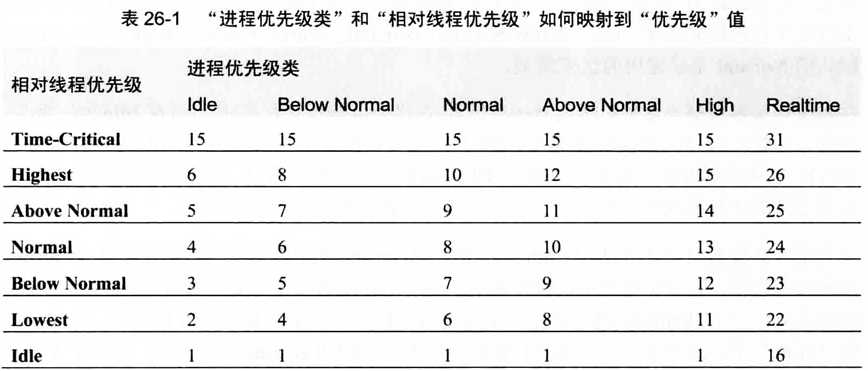
CLR终结器以线程Time-Critical优先级运行。
设置Thread的Priority属性向其传递ThreadPriority枚举类型定义的5个值来控制线程优先级。
一个进程中所有的前台线程停止时,所有的后台线程会立刻被终止。
每个AppDomain都可以运行一个单独应用程序,该应用程序有自己前台线程。所有前台线程都停止的时候,进程才会退出销毁。
线程可以从前台线程编程后台线程或则反向。应用程序主线程以及通过构造一个Thread对象显式创建的任何线程都默认为前台线程。线程池的线程都默认为后台线程。进入托管环境的本机代码创建的线程都是后台线程。
每个CLR拥有一个线程池,也就是一个线程池为该CLR控制的所有AppDomain共享。
CLR的工作模式:
ThreadPool定义的异步方法和回调委托:
static Boolean QueueUserWorkItem(WaitCallback callBack);static Boolean QueueUserWorkItem(WaitCallback callBack,Object state);delegate void WaitCallback(Object state);//执行ExecutionContexts.Go();internal static class ThreadPoolDemo { public static void Go() { Console.WriteLine("Main thread: queuing an asynchronous operation"); ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(ComputeBoundOp, 5); Console.WriteLine("Main thread: Doing other work here..."); Thread.Sleep(10000); // Simulating other work (10 seconds) Console.ReadLine(); } // This method's signature must match the WaitCallback delegate private static void ComputeBoundOp(Object state) { // This method is executed by a thread pool thread Console.WriteLine("In ComputeBoundOp: state={0}", state); Thread.Sleep(1000); // Simulates other work (1 second) // When this method returns, the thread goes back // to the pool and waits for another task }}//结果Main thread: queuing an asynchronous operationMain thread: Doing other work here...In ComputeBoundOp: state=5每个线程都关联一个执行上下文(Execution context),执行上下文包括很多东西:安全设置,宿主设置,上下文数据。
每当初始线程使用辅助线程执行任务时,初始线程的执行上下文会复制到辅助线程,保证辅助线程使用相同的安全设置和宿主设置,但这一操作会影响性能。
System.Threading.ExecutionContext类可以对执行上下文的复制功能进行控制:
public sealed class ExecutionContext:IDisposable, ISerializabel{ [SecurityCritical] public static AsyncFlowControl SuppressFlow(); public static void RestoreFlow(); public static Boolean IsFlowSuppressed(); // 未列出不常用的方法}阻止执行上下文可以显著提升服务器应用程序,而客户端应用程序提升不明显。
//调用ExecutionContexts.Go();internal static class ExecutionContexts { public static void Go() { // Put some data into the Main thread’s logical call context CallContext.LogicalSetData("Name", "Jeffrey"); // Initiate some work to be done by a thread pool thread // The thread pool thread can access the logical call context data ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem( state => Console.WriteLine("Name={0}", CallContext.LogicalGetData("Name"))); // Suppress the flowing of the Main thread’s execution context ExecutionContext.SuppressFlow(); // Initiate some work to be done by a thread pool thread // The thread pool thread can NOT access the logical call context data ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem( state => Console.WriteLine("Name={0}", CallContext.LogicalGetData("Name"))); // Restore the flowing of the Main thread’s execution context in case // it employs more thread pool threads in the future ExecutionContext.RestoreFlow(); SecurityExample(); } private static void SecurityExample() { ProxyType highSecurityObject = new ProxyType(); highSecurityObject.AttemptAccess("High"); // Works OK PermissionSet grantSet = new PermissionSet(PermissionState.None); grantSet.AddPermission(new SecurityPermission(SecurityPermissionFlag.Execution)); AppDomain lowSecurityAppDomain = AppDomain.CreateDomain("LowSecurity", null, new AppDomainSetup() { ApplicationBase = AppDomain.CurrentDomain.BaseDirectory }, grantSet, null); ProxyType lowSecurityObject = (ProxyType)lowSecurityAppDomain.CreateInstanceAndUnwrap(typeof(ProxyType).Assembly.ToString(), typeof(ProxyType).FullName); lowSecurityObject.DoSomething(highSecurityObject); Console.ReadLine(); } public sealed class ProxyType : MarshalByRefObject { // This method executes in the low-security AppDomain public void DoSomething(ProxyType highSecurityObject) { AttemptAccess("High->Low"); // Throws // Attempt access from the high-security AppDomain via the low-security AppDomain: Throws highSecurityObject.AttemptAccess("High->Low->High"); // Have the high-security AppDomain via the low-security AppDomain queue a work item to // the thread pool normally (without suppressing the execution context): Throws highSecurityObject.AttemptAccessViaThreadPool(false, "TP (with EC)->High"); // Wait a bit for the work item to complete writing to the console before starting the next work item Thread.Sleep(1000); // Have the high-security AppDomain via the low-security AppDomain queue a work item to // the thread pool suppressing the execution context: Works OK highSecurityObject.AttemptAccessViaThreadPool(true, "TP (no EC)->High"); } public void AttemptAccessViaThreadPool(Boolean suppressExecutionContext, String stack) { // Since the work item is queued from the high-security AppDomain, the thread pool // thread will start in the High-security AppDomain with the low-security AppDomain's // ExecutionContext (unless it is suppressed when queuing the work item) using (suppressExecutionContext ? (IDisposable)ExecutionContext.SuppressFlow() : null) { ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(AttemptAccess, stack); } } public void AttemptAccess(Object stack) { String domain = AppDomain.CurrentDomain.IsDefaultAppDomain() ? "HighSecurity" : "LowSecurity"; Console.Write("Stack={0}, AppDomain={1}, Username=", stack, domain); try { Console.WriteLine(Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("USERNAME")); } catch (SecurityException) { Console.WriteLine("(SecurityException)"); } } }}//结果Name=JeffreyName=Stack=High, AppDomain=HighSecurity, Username=dujinfengStack=High->Low, AppDomain=LowSecurity, Username=(SecurityException)Stack=High->Low->High, AppDomain=HighSecurity, Username=(SecurityException)Stack=TP (with EC)->High, AppDomain=HighSecurity, Username=(SecurityException)Stack=TP (no EC)->High, AppDomain=HighSecurity, Username=dujinfeng协作式取消就是需要显式调用取消。
怎样显式调用取消:
public sealed class CancellationTokenSource:IDisposable //引用类型{ public CancellationTokenSource(); public void Dispose();//释放资源比如WaitHandle public Boolean IsCancellationRequested {get;} public void Cancel(); public void Cancel(Boolean throwOnFirstException);}CancellationToken轻量级值类型,有一个字段包含对CancellationTokenSource对象的引用
public struct CancellationToken //一个值类型{ public static CancellationToken None {get;} //很好用 public Boolean IsCancellationRequested {get;} //通过非Task调用的操作调用 public void ThrowIfCancellationRequested();//通过Task调用的操作调用 // CancellationTokenSource取消时,WaitHandIe会收到信号 public WaitHandle WaitHandle {get;} //GetHashCode,Equals,operator==和operaor!=成员未列出 public Boolean CanBeCanceLed {get;}//很少使用 public CancellationTokenRegistration Register(Action<Object> callback, Object state, Boolean useSynchromzatronContext);//未列出更简单的重载版本}TaskDemo.Go();internal static class CancellationDemo { public static void Go() { CancellingAWorkItem(); Register(); Linking(); } private static void CancellingAWorkItem() { CancellationTokenSource cts = new CancellationTokenSource(); // Pass the CancellationToken and the number-to-count-to into the operation ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(o => Count(cts.Token, 1000)); Console.WriteLine("Press <Enter> to cancel the operation."); Console.ReadLine(); cts.Cancel(); // If Count returned already, Cancel has no effect on it // Cancel returns immediately, and the method continues running here... Console.ReadLine(); // For testing purposes } private static void Count(CancellationToken token, Int32 countTo) { for (Int32 count = 0; count < countTo; count++) { if (token.IsCancellationRequested) { Console.WriteLine("Count is cancelled"); break; // Exit the loop to stop the operation } Console.WriteLine(count); Thread.Sleep(200); // For demo, waste some time } Console.WriteLine("Count is done"); } private static void Register() { var cts = new CancellationTokenSource(); cts.Token.Register(() => Console.WriteLine("Canceled 1")); cts.Token.Register(() => Console.WriteLine("Canceled 2")); // To test, let's just cancel it now and have the 2 callbacks execute cts.Cancel(); } private static void Linking() { // Create a CancellationTokenSource var cts1 = new CancellationTokenSource(); cts1.Token.Register(() => Console.WriteLine("cts1 canceled")); // Create another CancellationTokenSource var cts2 = new CancellationTokenSource(); cts2.Token.Register(() => Console.WriteLine("cts2 canceled")); // Create a new CancellationTokenSource that is canceled when cts1 or ct2 is canceled /* Basically, Constructs a new CTS and registers callbacks with all he passed-in tokens. Each callback calls Cancel(false) on the new CTS */ var ctsLinked = CancellationTokenSource.CreateLinkedTokenSource(cts1.Token, cts2.Token); ctsLinked.Token.Register(() => Console.WriteLine("linkedCts canceled")); // Cancel one of the CancellationTokenSource objects (I chose cts2) cts2.Cancel(); // Display which CancellationTokenSource objects are canceled Console.WriteLine("cts1 canceled={0}, cts2 canceled={1}, ctsLinked canceled={2}", cts1.IsCancellationRequested, cts2.IsCancellationRequested, ctsLinked.IsCancellationRequested); }}//结果不可取消操作可以使用CancellationToken的静态None属性。该属性返回一个特殊的CancellationToken对象,该对象的IsCancellationRequest总是返回false。
可调用CancellationTokenSource的Register方法注册一个在线程取消时调用的方法。向该方法传递一个Action<Object>委托和一个bool值(名为useSynchronizationContext),bool值用来控制是否使用调用线程(false:调用register的线程)的SynchronizationContext(回调方法会被send(同步调用)给它,而不是post(异步调用))来调用委托,使用为true,不使用为false,如果不使用回调方法会被顺序执行。
Rigister中注册多个回调方法发生异常,要看一下CancellationTokenSource的Cancel方法,如果向该方法传递true,那么异常会阻塞回调方法的调用,如果是false,回调方法不会被阻塞,所有异常会被添加到集合中。该集合在Cancel抛出异常AggregateException的实例InnerExceptions属性中
Register方法返回一个CancellationTokenRegistration对象。
public struct CancellationTokenRegistration:{ IEquatable<CancellationTokenRegistration>, IDisposable { public void Dispose(); // GetHashCode, Equals, operator==和operator!=成员未列出 }}调用其Dispose可以取消回调函数调用。
可以使用CancellationTokenSource的CreateLinkedTokenSource方法连接一个CancellationTokenSource对象,返回一个CancellationTokenSource对象,任何一个对象被取消新的对象就会被取消。
CancellationDemo.Go();internal static class CancellationDemo { public static void Go() { CancellingAWorkItem(); Register(); Linking(); } private static void CancellingAWorkItem() { CancellationTokenSource cts = new CancellationTokenSource(); // Pass the CancellationToken and the number-to-count-to into the operation ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(o => Count(cts.Token, 1000)); Console.WriteLine("Press <Enter> to cancel the operation."); Console.ReadLine(); cts.Cancel(); // If Count returned already, Cancel has no effect on it // Cancel returns immediately, and the method continues running here... Console.ReadLine(); // For testing purposes } private static void Count(CancellationToken token, Int32 countTo) { for (Int32 count = 0; count < countTo; count++) { if (token.IsCancellationRequested) { Console.WriteLine("Count is cancelled"); break; // Exit the loop to stop the operation } Console.WriteLine(count); Thread.Sleep(200); // For demo, waste some time } Console.WriteLine("Count is done"); } private static void Register() { var cts = new CancellationTokenSource(); cts.Token.Register(() => Console.WriteLine("Canceled 1")); cts.Token.Register(() => Console.WriteLine("Canceled 2")); // To test, let's just cancel it now and have the 2 callbacks execute cts.Cancel(); } private static void Linking() { // Create a CancellationTokenSource var cts1 = new CancellationTokenSource(); cts1.Token.Register(() => Console.WriteLine("cts1 canceled")); // Create another CancellationTokenSource var cts2 = new CancellationTokenSource(); cts2.Token.Register(() => Console.WriteLine("cts2 canceled")); // Create a new CancellationTokenSource that is canceled when cts1 or ct2 is canceled /* Basically, Constructs a new CTS and registers callbacks with all he passed-in tokens. Each callback calls Cancel(false) on the new CTS */ var ctsLinked = CancellationTokenSource.CreateLinkedTokenSource(cts1.Token, cts2.Token); ctsLinked.Token.Register(() => Console.WriteLine("linkedCts canceled")); // Cancel one of the CancellationTokenSource objects (I chose cts2) cts2.Cancel(); // Display which CancellationTokenSource objects are canceled Console.WriteLine("cts1 canceled={0}, cts2 canceled={1}, ctsLinked canceled={2}", cts1.IsCancellationRequested, cts2.IsCancellationRequested, ctsLinked.IsCancellationRequested); }}//结果Press <Enter> to cancel the operation.0123Count is cancelledCount is doneCanceled 2Canceled 1linkedCts canceledcts2 canceledcts1 canceled=False, cts2 canceled=True, ctsLinked canceled=True请按任意键继续. . .CancellationTokenSource提供了指定时间后自动取消的对象方法CancelAfter:
public sealed class CancellationTokenSource:IDisposab1e{//一个引用类型public CancellationTokenSource(Int32 millisecondsDeiay):public CancellationTokenSource (TimeSpandelay);public void CancelAfter (Int32 millisecondsDeiay);public Void CancelAfter (TimeSpandelay);}ThreadPool的QueueUserWorkItem方法的弊端
System.Threading.Tasks可以解决这些问题。
private static void UsingTaskInsteadOfQueueUserWorkItem() { ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(ComputeBoundOp, 5); new Task(ComputeBoundOp, 5).Start(); Task.Run(() => ComputeBoundOp(5)); }Task构造函数接收一个Action或Action<Object>委托,静态方法Run需要传递一个Action或Func<TResult>委托。
还可以使用TaskCreationOptions标志来控制Task的执行。

private static void WaitForResult() { // Create and start a Task Task<Int32> t = new Task<Int32>(n => Sum((Int32)n), 10000); // You can start the task sometime later t.Start(); // Optionally, you can explicitly wait for the task to complete t.Wait(); // FYI: Overloads exist accepting a timeout/CancellationToken // Get the result (the Result property internally calls Wait) Console.WriteLine("The sum is: " + t.Result); // An Int32 value }Task<TResult>对象可以获得Task返回的结果。
Wait会使调用Wait的线程阻塞,等待Task结束,如果Task没有开始就用调用Wait线程执行Task。
如果Task任务抛出异常,不会被阻塞,直接存储到异常集合中,在t.Wait或t.Result会抛出System.AggregateException异常。该异常的InnerExceptions(返回ReadOnlyCollection<Exception>)和InnerException(从Exception集成)
System.AggregateException的一些功能:
如果不调用Wait或Result方法或不查询task的Exception属性,就不会注意到异常,可以向TaskSchedule的静态UnobservedTaskException事件登记一个回调方法,如果在task被垃圾回收时发现有没有被注意的异常,会触发这个事件,并传递一个UnobservedTaskException对象,其包含一个AggregateException对象。
private static void UnobservedException() { TaskScheduler.UnobservedTaskException += (sender, e) => { //e.SetObserved(); Console.WriteLine("Unobserved exception {0}", e.Exception, e.Observed); }; Task parent = Task.Factory.StartNew(() => { Task child = Task.Factory.StartNew(() => { throw new InvalidOperationException(); }, TaskCreationOptions.AttachedToParent); // Child’s exception is observed, but not from its parent child.ContinueWith((task) => { var _error = task.Exception; }, TaskContinuationOptions.OnlyOnFaulted); }); // If we do not Wait, the finalizer thread will throw an unhandled exception terminating the process //parent.Wait(); // throws AggregateException(AggregateException(InvalidOperationException)) parent = null; Console.ReadLine(); // Wait for the tasks to finish running GC.Collect(); Console.ReadLine(); }//结果/*Unobserved exception System.AggregateException: 未通过等待任务或访问任务的 Exception 属性观察到任务的异常。因此,终结器 线程重新引发了未观察到的异常。 ---> System.AggregateException: 发生一个或多个错误。 ---> System.InvalidOperationException: 对象的当前状态使该操作无效。 在 TaskDemo.<>c.<UnobservedException>b__8_2() 位置 C:\Users\dujinfeng\Desktop\NetCLRVia\CLR-via-C-4th-Edition-Code\Ch27-1-ComputeOps.cs:行号 355 在 System.Threading.Tasks.Task.InnerInvoke() 在 System.Threading.Tasks.Task.Execute() --- 内部异常堆栈跟踪的结尾 --- --- 内部异常堆栈跟踪的结尾 ------> (内部异常 #0) System.AggregateException: 发生一个或多个错误。 ---> System.InvalidOperationException: 对象的当前状态使该操作无效。 在 TaskDemo.<>c.<UnobservedException>b__8_2() 位置 C:\Users\dujinfeng\Desktop\NetCLRVia\CLR-via-C-4th-Edition-Code\Ch27-1-ComputeOps.cs:行号 355 在 System.Threading.Tasks.Task.InnerInvoke() 在 System.Threading.Tasks.Task.Execute() --- 内部异常堆栈跟踪的结尾 ------> (内部异常 #0) System.InvalidOperationException: 对象的当前状态使该操作无效。 在 TaskDemo.<>c.<UnobservedException>b__8_2() 位置 C:\Users\dujinfeng\Desktop\NetCLRVia\CLR-via-C-4th-Edition-Code\Ch27-1-ComputeOps.cs:行号 355 在 System.Threading.Tasks.Task.InnerInvoke() 在 System.Threading.Tasks.Task.Execute()<---<---*/请按任意键继续. . .Task还提供了两个静态方法,允许等待一个Task对象数组
private static void Cancel() { CancellationTokenSource cts = new CancellationTokenSource(); Task<Int32> t = Task.Run(() => Sum(cts.Token, 10000), cts.Token); // Sometime later, cancel the CancellationTokenSource to cancel the Task cts.Cancel();//这是一个异步请求 try { // If the task got canceled, Result will throw an AggregateException Console.WriteLine("The sum is: " + t.Result); // An Int32 value } catch (AggregateException ae) { // Consider any OperationCanceledException objects as handled. // Any other exceptions cause a new AggregateException containing // only the unhandled exceptions to be thrown ae.Handle(e => e is OperationCanceledException); // If all the exceptions were handled, the following executes Console.WriteLine("Sum was canceled"); } } private static Int32 Sum(CancellationToken ct, Int32 n) { Int32 sum = 0; for (; n > 0; n--) { // The following line throws OperationCanceledException when Cancel // is called on the CancellationTokenSource referred to by the token ct.ThrowIfCancellationRequested(); //Thread.Sleep(0); // Simulate taking a long time checked { sum += n; } } return sum; }wait和result都可能会阻塞调用线程,可以使用ContinueWith来使得任务完成启动另一个Task,做Task完成做的事情。
private static void ContinueWith() { // Create and start a Task, continue with another task Task<Int32> t = Task.Run(() => Sum(10000)); // ContinueWith returns a Task but you usually don't care Task cwt = t.ContinueWith(task => Console.WriteLine("The sum is: " + task.Result)); cwt.Wait(); // For the testing only } private static Int32 Sum(Int32 n) { Int32 sum = 0; for (; n > 0; n--) checked { sum += n; } return sum; }如果在调用ContinueWith之前Task已经完成,直接显示结果。
Task对象内部包含ContinueWith任务的集合,Task可以多次调用ContinueWith方法,在调用ContunueWith时可以传递TaskContinuationOptions枚举来控制Task任务。
[Flags,Serializab1e]public enum TaskContinuationOptions{None = 0x0000,//默认//提议TaskSchedu1er你希望该任务尽快执行,PreferFairness = 0x0001,//提议TaskSchedu1er应尽可能地创建线程池线程LongRunning = 0x0002,//该提议总是被采纳:将一个Task和它的父Task关联(稍后讨论)AttachedToParent =0x0004,//任务试图和这个父任务连接将抛出一个invalidOperationExceptionDenyChi1dAttach = 0x0008,//强迫了任务使用默认调度器而不是父仃务的调度器HideScheduler = 0x0010,//除非前置任务(antecedent task)完成,否则禁正延续任务完成(取消)LazyCance11ation = 0x0020,//这个标志指出你希望由执行第一个任务的线程执行//ContinueWith任务。第一个任务完成后,调用//continuewith的线程接着执行ContinueWith任务ExecuteSynchronously = 0x80000,//这些标志指出在什么情况下运行ContinueWith任务NotOnRanToComp1etion = 0x10000,NotOnFaulted = 0x20000,NotOnCance1ed = 0x4000,//这些标志是以上三个标志的便利组合OnlyOnCance1ed = NotOnRanToCompletion|NotOnFaulted,OnlyOnFau1ted = NotOnRanToCompletion|NotOnCance1ed,OnlyOnRanToComp1etion = NotOnFaulted|NotOnCanceled,} private static void MultipleContinueWith() { // Create and start a Task, continue with multiple other tasks Task<Int32> t = Task.Run(() => Sum(10000)); // Each ContinueWith returns a Task but you usually don't care t.ContinueWith(task => Console.WriteLine("The sum is: " + task.Result), TaskContinuationOptions.OnlyOnRanToCompletion); t.ContinueWith(task => Console.WriteLine("Sum threw: " + task.Exception), TaskContinuationOptions.OnlyOnFaulted); t.ContinueWith(task => Console.WriteLine("Sum was canceled"), TaskContinuationOptions.OnlyOnCanceled); try { t.Wait(); // For the testing only } catch (AggregateException) { } } private static void ParentChild() { Task<Int32[]> parent = new Task<Int32[]>(() => { var results = new Int32[3]; // Create an array for the results // This tasks creates and starts 3 child tasks new Task(() => results[0] = Sum(10000), TaskCreationOptions.AttachedToParent).Start(); new Task(() => results[1] = Sum(20000), TaskCreationOptions.AttachedToParent).Start(); new Task(() => results[2] = Sum(30000), TaskCreationOptions.AttachedToParent).Start(); // Returns a reference to the array (even though the elements may not be initialized yet) return results; }); // When the parent and its children have run to completion, display the results var cwt = parent.ContinueWith(parentTask => Array.ForEach(parentTask.Result, Console.WriteLine)); // Start the parent Task so it can start its children parent.Start(); cwt.Wait(); // For testing purposes } private static Int32 Sum(Int32 n) { Int32 sum = 0; for (; n > 0; n--) checked { sum += n; } return sum; }Task对象是很消耗资源,如果不需要一些额外的功能ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem的利用率更高。
Task的组成:
public enum TaskStatus{//这些标志指出一个Task在其生命期内的状态Created,//任务己显式创建:可以手动start()这个任务WaitingForActivation,//任务已隐式创建;会自动开始WaitingToRun,//任务己调度,但尚未运行Running,//任务正在运行WaitingForChildrenToComplete,//任务正在等待它的子任务完成,子任务完成后它才完成//任务的最终状态是以下三个之一:RanToCompletion,Canceled,Faulted}Task和Task<TResult>实现了IDisposable接口,Dispose主要内容是关闭ManualResetEventSlim,建以不要显示调用。
Task工厂主要是启动一组相同配置和相同参数的Tasks设计的。TaskFactory<Int32>,创建Task<Int32>的工厂,共同享有CancellationTokenSource标记,创建的所有延续Task都以同步方式进行,所有Task对象都使用默认TaskScheduler。
private static void TaskFactory() { Task parent = new Task(() => { var cts = new CancellationTokenSource(); var tf = new TaskFactory<Int32>(cts.Token, TaskCreationOptions.AttachedToParent, TaskContinuationOptions.ExecuteSynchronously, TaskScheduler.Default); // 启动taskfactory创建3个子任务 var childTasks = new[] { tf.StartNew(() => Sum(cts.Token, 10000)), tf.StartNew(() => Sum(cts.Token, 20000)), tf.StartNew(() => Sum(cts.Token, Int32.MaxValue)) // Too big, throws OverflowException }; // 任何子任务抛出异常,就取消其余子任务 for (Int32 task = 0; task < childTasks.Length; task++) childTasks[task].ContinueWith(t => cts.Cancel(), TaskContinuationOptions.OnlyOnFaulted); // 所有子任务完成后,从未出错/未取消的任务获取返回的最大值 // 然后将最大值传给另一个task来显示最大结果 tf.ContinueWhenAll( childTasks, completedTasks => completedTasks.Where(t => t.Status == TaskStatus.RanToCompletion).Max(t => t.Result), CancellationToken.None) .ContinueWith(t => Console.WriteLine("The maximum is: " + t.Result), TaskContinuationOptions.ExecuteSynchronously).Wait(); // 等待测试 }); // 子任务完成后,也显示任何未处理的异常 parent.ContinueWith(p => { // 所有文本放到一个StringBuilder中,并只调用Console.WriteLine一次 // 因为这个任务可能和上面的任务并行执行 StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder("The following exception(s) occurred:" + Environment.NewLine); foreach (var e in p.Exception.Flatten().InnerExceptions) sb.AppendLine(" " + e.GetType().ToString()); Console.WriteLine(sb.ToString()); }, TaskContinuationOptions.OnlyOnFaulted); // 启动父任务,使它能启动子任务 parent.Start(); try { parent.Wait(); // For testing purposes } catch (AggregateException) { } } private static Int32 Sum(CancellationToken ct, Int32 n) { Int32 sum = 0; for (; n > 0; n--) { // The following line throws OperationCanceledException when Cancel // is called on the CancellationTokenSource referred to by the token ct.ThrowIfCancellationRequested(); //Thread.Sleep(0); // Simulate taking a long time checked { sum += n; } } return sum; }FCL提供了两个从TaskScheduler类型派生的调度器:线程调度器(thread pool task scheduler)和同步上下文调度器(synchronization context task scheduler)。默认使用线程调度器。
同步上下文调度器更适合GUI程序。该调度器不适用线程池,通过TaskScheduler.FormCurretSynchronizationContext方法获得该调度器。
private static void SynchronizationContextTaskScheduler() { var f = new MyForm(); System.Windows.Forms.Application.Run(); } private sealed class MyForm : System.Windows.Forms.Form { private readonly TaskScheduler m_syncContextTaskScheduler; public MyForm() { // Get a reference to a synchronization context task scheduler m_syncContextTaskScheduler = TaskScheduler.FromCurrentSynchronizationContext(); Text = "Synchronization Context Task Scheduler Demo"; Visible = true; Width = 400; Height = 100; } private CancellationTokenSource m_cts; protected override void OnMouseClick(System.Windows.Forms.MouseEventArgs e) { if (m_cts != null) { // An operation is in flight, cancel it m_cts.Cancel(); m_cts = null; } else { // An operation is not in flight, start it Text = "Operation running"; m_cts = new CancellationTokenSource(); // This task uses the default task scheduler and executes on a thread pool thread Task<Int32> t = Task.Run(() => Sum(m_cts.Token, 20000), m_cts.Token); // These tasks use the synchronization context task scheduler and execute on the GUI thread t.ContinueWith(task => Text = "Result: " + task.Result, CancellationToken.None, TaskContinuationOptions.OnlyOnRanToCompletion, m_syncContextTaskScheduler); t.ContinueWith(task => Text = "Operation canceled", CancellationToken.None, TaskContinuationOptions.OnlyOnCanceled, m_syncContextTaskScheduler); t.ContinueWith(task => Text = "Operation faulted", CancellationToken.None, TaskContinuationOptions.OnlyOnFaulted, m_syncContextTaskScheduler); } base.OnMouseClick(e); } } private static Int32 Sum(CancellationToken ct, Int32 n) { Int32 sum = 0; for (; n > 0; n--) { // The following line throws OperationCanceledException when Cancel // is called on the CancellationTokenSource referred to by the token ct.ThrowIfCancellationRequested(); //Thread.Sleep(0); // Simulate taking a long time checked { sum += n; } } return sum; }Parallel Extensions Extras 提供了额外的调度器
多个方法并行或顺序执行,使用线程池,内部使用Task。同时调用线程会将自己挂起,直到所有工作完成。任何一个Task出现异常,都会抛出AggregateException异常。多个线程需要添加线程同步锁保护共享数据。
private static void SimpleUsage() { // One thread performs all this work sequentially for (Int32 i = 0; i < 1000; i++) DoWork(i); // The thread pool’s threads process the work in parallel Parallel.For(0, 1000, i => DoWork(i)); var collection = new Int32[0]; // One thread performs all this work sequentially foreach (var item in collection) DoWork(item); // The thread pool’s threads process the work in parallel Parallel.ForEach(collection, item => DoWork(item)); // One thread executes all the methods sequentially Method1(); Method2(); Method3(); // The thread pool’s threads execute the methods in parallel Parallel.Invoke( () => Method1(), () => Method2(), () => Method3()); } private static void DoWork(Int32 i) { } private static void Method1() { } private static void Method2() { } private static void Method3() { }ParallelOptions对象用于控制Parallel
public class ParallelOptions{ public ParallelOptions(); //允许取消操作 public CancellationToken CancellationToken{get;set;}//默认为CancellationToken.None //允许指定可以并发操作的最大工作项数目 public Int32MaxDegreeOfParallelism {get;set;}//默认为-1(可用CPU数) //允许指定要使用哪个TaskScheduler public TaskSchedulerTaskScheduler {get;set;}//默认为TaskScheduler.Default}有一些For和Foreach的重载版本允许3个委托
计算一个目录中所有文件字节的长度.
String path = Environment.GetFolderPath(Environment.SpecialFolder.MyDocuments); Console.WriteLine("The total bytes of all files in {0} is {1:N0}.", path, DirectoryBytes(@path, "*.*", SearchOption.TopDirectoryOnly)); private static Int64 DirectoryBytes(String path, String searchPattern, SearchOption searchOption) { var files = Directory.EnumerateFiles(path, searchPattern, searchOption); Int64 masterTotal = 0; ParallelLoopResult result = Parallel.ForEach<String, Int64>(files, () => { // localInit: 每个任务开始之前调用一次 // 每个任务开始之前,总计值都初始化为0 return 0; // 将taskLocalTotal初始值为 0 }, (file, parallelLoopState, index, taskLocalTotal) => { // body: 每个工作项调用一次 // 获得这个文件的大小,把它添加到这个任务的累加值上 Int64 fileLength = 0; FileStream fs = null; try { fs = File.OpenRead(file); fileLength = fs.Length; } catch (IOException) { /* Ignore any files we can't access */ } finally { if (fs != null) fs.Dispose(); } return taskLocalTotal + fileLength; }, taskLocalTotal => { // 每个任务完成时调用 //将这个任务的总计值taskLocalTotal添加到总的总计值mastertotal上 Interlocked.Add(ref masterTotal, taskLocalTotal); }); return masterTotal; } //结果The total bytes of all files in C:\Users\dujinfeng\Documents is 2,698.请按任意键继续. . .委托主体传递了一个ParallelLoopState对象,可以通过该对象与参与工作的其他任务进行交互,Stop方法使得循环停止,Break方法使得循环不再处理当前项之后的项.LoweatBreakIteration属性返回处理过程中调用过Break方法的最低项,如果没有break过,就返回null.
public calss ParallelLoopState{ public void Stop(); public Boolean IsStopped{ get; } public void Break(); public Int64? LowestBreakIteration{ get; } public Boolean IsExceptional{ get; } public Boolean ShouldExitCurrentIteration{ get; }}在处理任何一项任务造成了异常,IsException属性会返回true,如果调用过Stop,Break,CancellationTokenSource,查询ShouldExitCurrentIteration就会返回true。
For和ForEach会返回ParalleLoopResult实例,
public struct ParallelLoopResult{ //如果操作提提前终止,以下方法返回false public Boolean IsCompleted{get;} public INt64? LowestBreakIteration{get;}}如果正常运行完IsCompleted返回true。
顺序查询和并行查询(Parallel LINQ),System.Linq.ParallelEnumerable类实现了PLINQ的所有功能。PatallelEnumerable的AsParallel扩展方法可以将顺序查询(基于IEnumerable或者IEnumerable<T>)转换成并行查询(基于ParallelQuery或ParallelQuery<T>)
public static ParallelQuery<TSource> AsParallel<TSource>(this IEnumerable<TSource> source);public static ParallelQuery AsParallel(this IEnumerable source);例子返回一个程序集所有过时(obsolete)方法
//调用ObsoleteMethods(typeof(Object).Assembly); private static void ObsoleteMethods(Assembly assembly) { var query = from type in assembly.GetExportedTypes().AsParallel() from method in type.GetMethods(BindingFlags.Public | BindingFlags.Instance | BindingFlags.Static) let obsoleteAttrType = typeof(ObsoleteAttribute) where Attribute.IsDefined(method, obsoleteAttrType) orderby type.FullName let obsoleteAttrObj = (ObsoleteAttribute) Attribute.GetCustomAttribute(method, obsoleteAttrType) select String.Format("Type={0}\nMethod={1}\nMessage={2}\n", type.FullName, method.ToString(), obsoleteAttrObj.Message); // Display the results foreach (var result in query) Console.WriteLine(result); // Alternate (not as fast): query.ForAll(Console.WriteLine); }//结果Type=Microsoft.Win32.RegistryHiveMethod=System.String ToString(System.IFormatProvider)Message=The provider argument is not used. Please use ToString().Type=Microsoft.Win32.RegistryHiveMethod=System.String ToString(System.String, System.IFormatProvider)Message=The provider argument is not used. Please use ToString(String).Type=Microsoft.Win32.RegistryKeyPermissionCheckMethod=System.String ToString(System.String, System.IFormatProvider)Message=The provider argument is not used. Please use ToString(String).Type=Microsoft.Win32.RegistryKeyPermissionCheckMethod=System.String ToString(System.IFormatProvider)Message=The provider argument is not used. Please use ToString().Type=Microsoft.Win32.RegistryOptionsMethod=System.String ToString(System.IFormatProvider)Message=The provider argument is not used. Please use ToString().ParallelEnumerable的AsSequential方法可以将并行查询转换成顺序查询。
public static IEnumerable<TSource> AsSequential<TSource> (this ParallelQuery<TSource> source)顺序查询中处理结果方法foreach在并行中可以用ParallelEnumerable的ForAll方法处理查询:
static void ForAll<TSource> (this ParallelQuery<TSource> source,Action<TSource> action);//上面例子的最后foreach可以被替换为:query.ForAll(Console.WriteLine);但调用Console.WriteLine并行执行没有意义,其内部让线程同步,同时只有一个线程能访问控制台。
如果需要并行执行并保持顺序可以使用ParallelEnumerable的AsOrdered方法,排序方法Orderby,OrderbyDescending,ThenBy,ThenByDescending。不排序的方法Distinct,Except,Intersect,Union,Join,GroupBy,GroupJoin,ToLookup。
并行用来控制查询的方法WithCancellation<TSource>,WithDegreeOfParallelism<TSource>,WithExecutionMode<TSource>,WithMergeOptions<TSource>方法。
调用Concat,ElementAt,FIrst,Last,Skip,Take,Zip,Select等可以调用WithExecutionMode,向其传递ParallelExecutionMode标志,强迫以并行执行。
public enum ParallelExceptionMode{ Default=0;//让并行Linq决定处理查询的最佳方式 ForceParallelism=1//强迫查询以其并行方式处理}并行处理,结果必须合并,可调用WithMergeOptions,向其传递ParallelMergeOptions标志,从而控制缓冲与合并方式
public enum ParallelMergeOptions{ Default=0,//目前和AutoBuffered一样 NotBuffered=1,//结果一旦就绪就开始处理,最省内存,速度比较慢 AutoBuffered=2,//每个线程在处理前缓冲一些结果,介于之间 FullyBuffered=3//每个线程在处理前缓冲所有结果,运行速度最快,内存使用多}System.Threading.Timer定时器构造函数
puniic sealed class Timer:MarshalByRefObject,IDisposable{ public Timer(TimerCa11back callback,0bject stater,Int32 dueTime,Int32 period); public Timer(TimerCallback callback,0bject state,UInt32 dueTime,UInt32 period); public Timer(TimerCallback callback,Object state,Int64 dueTime,Int64 period); public Timer(TimerCa1lback callback,0bject state,Timespan dueTime,TimeSpan Period);}//System.Threading.TimerCallbackdelegate void TimerCallback(Object state);在内部:所有Timer对象只使用一个线程,该线程知道Timer对象下一次什么时候到期,如果到期就会唤醒,调用ThreadPool的QueueUserWorkItem,
如果回调函数执行时间长,定时器有可能再次触发,造成多线程执行回调方法,针对这个问题,建以在构造Timer时,将period指定为Timeout.Infinite,这样只执行一次回调,在回调中使用Change指定新的dueTimer,并再次将Period执行Timeout.Infinite。
public sealed class Timer:MarshalByRefObject,IDisposabie{ public Boolean Change(Int32 dueTime,Int32 period); public Boolean Change(UInt32 dueTime,UInt32 period); public Boo1eam Change(Int64 dueTime,Int64 period); public Boolean Change(TimeSpan dueTime,Timespan period);}Timer类的Dispose方法完全取消计时器,在完成回调之后,向notifyObject参数标识的内核对象发出信号,
internal static class TimerDemo { private static Timer s_timer; public static void Go() { Console.WriteLine("Checking status every 2 seconds"); // Create the Timer ensuring that it never fires. This ensures that // s_timer refers to it BEFORE Status is invoked by a thread pool thread s_timer = new Timer(Status, null, Timeout.Infinite, Timeout.Infinite); // Now that s_timer is assigned to, we can let the timer fire knowing // that calling Change in Status will not throw a NullReferenceException s_timer.Change(0, Timeout.Infinite); Console.ReadLine(); // Prevent the process from terminating } // This method's signature must match the TimerCallback delegate private static void Status(Object state) { // This method is executed by a thread pool thread Console.WriteLine("In Status at {0}", DateTime.Now); Thread.Sleep(1000); // Simulates other work (1 second) // Just before returning, have the Timer fire again in 2 seconds s_timer.Change(2000, Timeout.Infinite); // When this method returns, the thread goes back // to the pool and waits for another work item }}//结果Checking status every 2 secondsIn Status at 2020-02-22 06:57:32In Status at 2020-02-22 06:57:35In Status at 2020-02-22 06:57:38In Status at 2020-02-22 06:57:41In Status at 2020-02-22 06:57:44还可以使用Task的Delay和async和await关键字来编码
internal static class DelayDemo { public static void Go() { Console.WriteLine("Checking status every 2 seconds"); Status(); Console.ReadLine(); // Prevent the process from terminating } // This method can take whatever parameters you desire private static async void Status() { while (true) { Console.WriteLine("Checking status at {0}", DateTime.Now); // Put code to check status here... // At end of loop, delay 2 seconds without blocking a thread await Task.Delay(2000); // await allows thread to return // After 2 seconds, some thread will continue after await to loop around } }}定时器类别
微软的线程池技术相当的好,工作情况非常理想,很难搞出一个比CLR更好的线程池。
设置最大线程数,最好不要设置上限,如果发生饥饿或死锁,那么这些线程都会被阻塞,如果设置上限,就会导致没有新的空闲线程执行任务。
System.Threading.ThreadPool类提供了一些静态方法:GetMaxThreads,SetMaxThreads,GetMinThreads,SetMinThreads和GetAvailableThreads方法,可以设置和查询线程数,强烈建以不要使用上诉的任何方法。
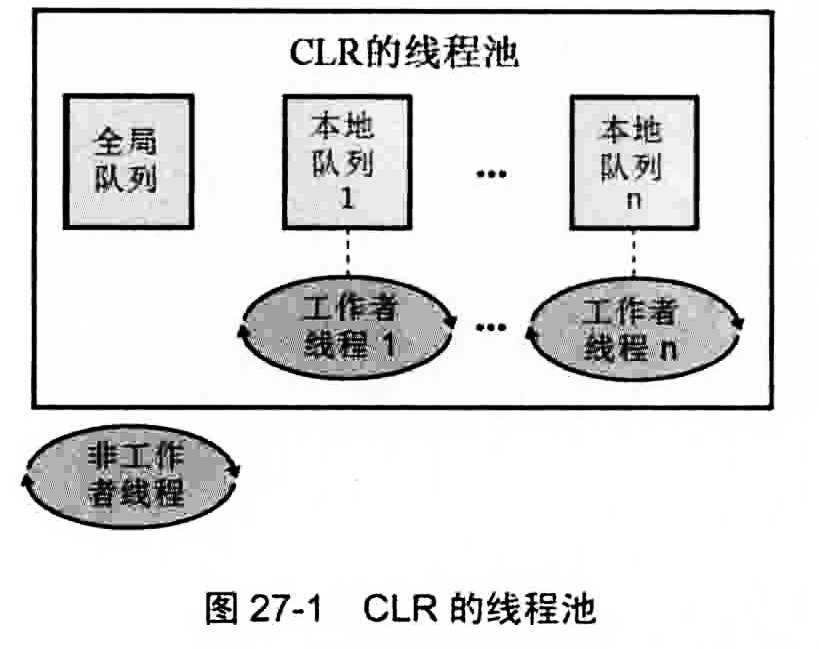
线程池的线程都是工作者线程,主要讲解一下ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem,Timer类和Task异步执行时线程池操作的异同点:
线程池默认创建CPU数量的工作线程,如果设置ThreadPool.SetMinThreads,则会创建设置值。
cpu 一般拥有多个核心和一个cpu内的缓存(一般是L2),缓存一般位于cpu芯片内, 他的速度远远高于主板上的内存,一般来说cpu会把数据从内存加载到缓存中 ,这样可以获得更好的性能(特别是频繁使用的数据),高速缓存默认划分64 Byte为一个区域(这个数字可能在不同的平台上不一样, 可以通过 ?win32 api 函数 GetProcessorInformation 修改),一个区域在一个时间点只允许一个核心操作,那么完全可能一个线程在操作field1 的时候 , 运行于另外一个cpu上的另外一个线程想操作field2,就必须等待线程1完成以后才能获取这个缓存区域的访问.
例子:显式布局,性能提高了80%
internal static class FalseSharing {#if true private class Data { // These two fields are right next to each other in // memory; most-likely in the same cache line public Int32 field1; public Int32 field2; }#else [StructLayout(LayoutKind.Explicit)] private class Data { // These two fields are right next to each other in // memory; most-likely in the same cache line [FieldOffset(0)] public Int32 field1; [FieldOffset(64)] public Int32 field2; }#endif private const Int32 iterations = 100000000; private static Int32 s_operations = 2; private static Stopwatch s_stopwatch; public static void Go() { Data data = new Data(); s_stopwatch = Stopwatch.StartNew(); ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(o => AccessData(data, 0)); ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(o => AccessData(data, 1)); Console.ReadLine(); } private static void AccessData(Data data, Int32 field) { for (Int32 x = 0; x < iterations; x++) if (field == 0) data.field1++; else data.field2++; if (Interlocked.Decrement(ref s_operations) == 0) Console.WriteLine("Access time: {0}", s_stopwatch.Elapsed); }}//结果,可能共享缓存Access time: 00:00:01.0554650//显式指定内存布局Access time: 00:00:00.2595376