在平常使用Android手机的时候,我们都知道,几乎每一个app都在/data/data/<相应的包名>的文件夹下保存数据。那这些数据怎么进行保存的呢?在这里,将简单的介绍一下。
1.将数据保存在文件中
Context类中有一个openFileOutPut方法,这个方法可以将我们的数据保存在data目录下的文件里面。
openFileOutput(String name, int mode)方法中带两个参数,第一个参数是文件名,这里只能写文件的名字,不能包含路径,因为所有的数据都保存在/data/data/<应用包名>/files/目录下;第二个参数是文件的操作模式,有MDOE_PRIVATE,MODE_APPEND,MODE_WORLD_READABLE和MODE_WORLD_WRITEABLE。
其中MODE_PRIVATE模式的是默认的操作模式,每一次写入的内容时,都会覆盖前面的内容;MODE_APPEND模式表示的是每次写入的内容追加在前面的后面;MODE_WORLD_READABLE表示的是其他应用程序可以对该文件进行写的操作;MODE_WORLD_WRITEABLE表示的是其他应用程序可以对该文件进行读的操作。不过在后面的两种模式过于危险,google已经在Android 4.2中废弃了。
openFileOutput()方法返回的是一个FileOutPutStream的对象,得到了这个对象,就可以使用Java的IO流来对文件的使用了。
1 public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity implements View.OnClickListener { 2 private Button mButton = null; 3 4 @Override 5 protected void onCreate(@Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) { 6 super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); 7 setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); 8 mButton = (Button) findViewById(R.id.id_button); 9 mButton.setOnClickListener(this);10 }11 12 @Override13 public void onClick(View v) {14 BufferedWriter bw = null;15 FileOutputStream fos = null;16 try {17 String string = "pby 的数据";18 fos = openFileOutput("pby", MODE_PRIVATE);19 bw = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(fos));20 bw.write(string);21 } catch (FileNotFoundException e) {22 e.printStackTrace();23 } catch (IOException e) {24 e.printStackTrace();25 } finally {26 if (bw != null) {27 try {28 bw.close();29 } catch (IOException e) {30 e.printStackTrace();31 }32 }33 if (fos != null) {34 try {35 fos.close();36 } catch (IOException e) {37 e.printStackTrace();38 }39 }40 41 }42 43 }44 }
1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> 2 <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" 3 android:layout_width="match_parent" 4 android:layout_height="match_parent" 5 android:gravity="center" 6 android:orientation="vertical"> 7 8 <Button 9 android:id="@+id/id_button"10 android:layout_width="match_parent"11 android:layout_height="wrap_content"12 android:text="保存" />13 </LinearLayout>
点击保存过后,就会把我们的数据保存在data目录下。
如果我们想要查看的话,就可以在Android studio(我是2.3.2的版本)中找到Tools->Android->Android Device Monitor
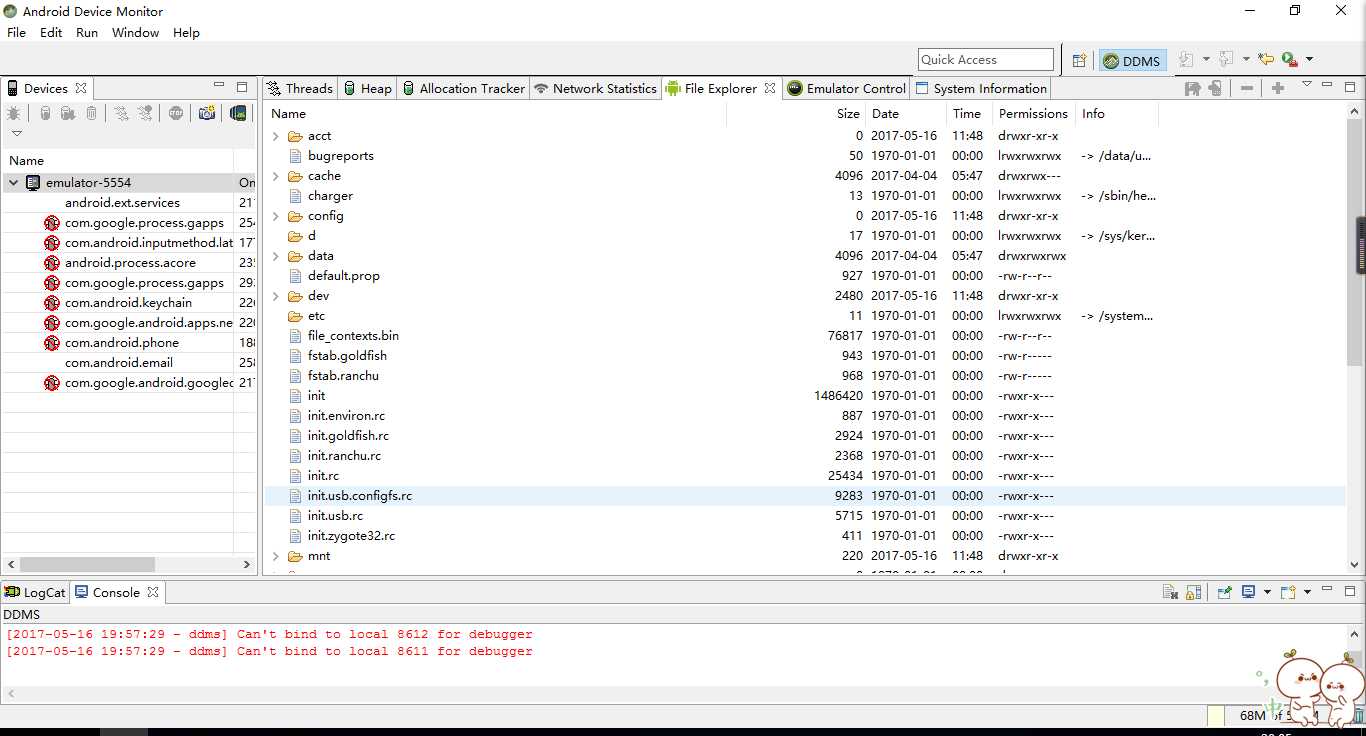
再打开/data/data/<应用包名>/files/,发现有一个文件,就是我们之前创建的一个文件。
我们可以点击 ,对相应的文件进行导出操作。
,对相应的文件进行导出操作。
注:
如果打开/data/文件夹是一个空的话,表示模拟器没有root,必须获得root权限。具体的操作会在后续的文章中介绍。
2.从文件中读取数据
在Context类中,与openFileOutput方法对应的是openFileInput方法,用户从data目录读取相应的数据。这个方法相较于openFileOutput方法简单一些。
1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> 2 <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" 3 android:layout_width="match_parent" 4 android:layout_height="match_parent" 5 android:gravity="center" 6 android:orientation="vertical"> 7 8 <Button 9 android:id="@+id/id_save"10 android:layout_width="match_parent"11 android:layout_height="wrap_content"12 android:text="保存" />13 14 <Button15 android:id="@+id/id_load"16 android:layout_width="match_parent"17 android:layout_height="wrap_content"18 android:text="加载" />19 <TextView20 android:id="@+id/id_textView"21 android:textSize="30sp"22 android:gravity="center"23 android:layout_width="match_parent"24 android:layout_height="100dp" />25 </LinearLayout>
1 package com.example.android_demo; 2 3 import android.os.Bundle; 4 import android.support.annotation.Nullable; 5 import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity; 6 import android.view.View; 7 import android.widget.Button; 8 import android.widget.TextView; 9 10 import java.io.BufferedReader; 11 import java.io.BufferedWriter; 12 import java.io.FileInputStream; 13 import java.io.FileNotFoundException; 14 import java.io.FileOutputStream; 15 import java.io.IOException; 16 import java.io.InputStreamReader; 17 import java.io.OutputStreamWriter; 18 19 20 public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity implements View.OnClickListener { 21 private Button mButtonSave = null; 22 private Button mButtonLoad = null; 23 private TextView mTextView = null; 24 @Override 25 protected void onCreate(@Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) { 26 super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); 27 setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); 28 mButtonSave = (Button) findViewById(R.id.id_save); 29 mButtonSave.setOnClickListener(this); 30 mButtonLoad = (Button) findViewById(R.id.id_load); 31 mButtonLoad.setOnClickListener(this); 32 mTextView = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.id_textView); 33 } 34 35 @Override 36 public void onClick(View v) { 37 switch (v.getId()) 38 { 39 case R.id.id_save: 40 { 41 save(); 42 break; 43 } 44 case R.id.id_load: 45 { 46 load(); 47 break; 48 } 49 } 50 51 } 52 private void save() 53 { 54 BufferedWriter bw = null; 55 FileOutputStream fos = null; 56 try { 57 String string = "pby 的数据"; 58 fos = openFileOutput("pby", MODE_PRIVATE); 59 bw = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(fos)); 60 bw.write(string); 61 } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { 62 e.printStackTrace(); 63 } catch (IOException e) { 64 e.printStackTrace(); 65 } finally { 66 if (bw != null) { 67 try { 68 bw.close(); 69 } catch (IOException e) { 70 e.printStackTrace(); 71 } 72 } 73 if (fos != null) { 74 try { 75 fos.close(); 76 } catch (IOException e) { 77 e.printStackTrace(); 78 } 79 } 80 81 } 82 } 83 private void load() 84 { 85 BufferedReader br = null; 86 FileInputStream fis = null; 87 try 88 { 89 String content = null; 90 fis = openFileInput("pby"); 91 br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(fis)); 92 content = br.readLine(); 93 mTextView.setText(content); 94 }catch(FileNotFoundException e) 95 { 96 e.printStackTrace(); 97 } catch (IOException e) { 98 e.printStackTrace(); 99 }100 finally{101 if(br != null)102 {103 try {104 br.close();105 } catch (IOException e) {106 e.printStackTrace();107 }108 }109 if(fis != null)110 {111 try {112 fis.close();113 } catch (IOException e) {114 e.printStackTrace();115 }116 }117 }118 }119 }
效果示意图